Is the installation of the Tuya Exit button complicated? Can ordinary users complete the installation by themselves? What are the precautions during the installation process?
Is the installation of the Tuya Exit button complicated? Can ordinary users complete the installation by themselves? What are the precautions during the installation process?
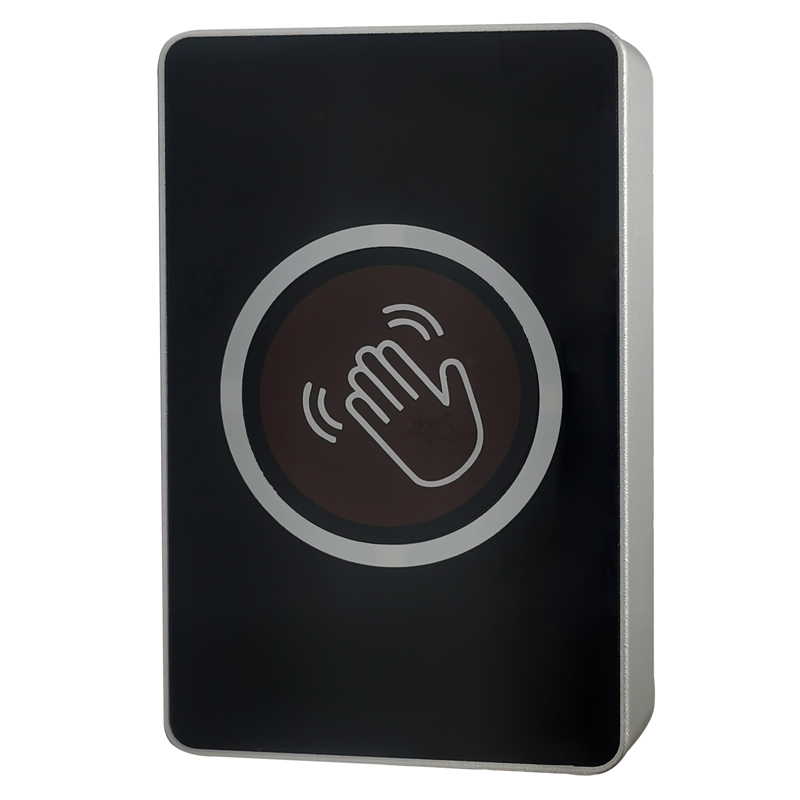
Installing the Tuya Exit Button: A Guide for Regular Users1. Installation Complexity
The Tuya Exit Button is crafted for straightforward installation. Regular users can put it in place without the need for professional help.
The installation process typically consists of these steps:
Mounting the Button: You can use screws or adhesive to attach the button to a wall or door frame.
Connecting Wires: It involves making connections to the access control device or door strike.
Testing the Functionality: Ensuring that the button can unlock the door as intended.
2. DIY Installation Feasibility
Yes, most users can install it on their own by following these steps:
Gather Necessary Tools: You'll need a screwdriver, wire strippers, and a voltage tester.
Refer to the Manual: The included manual offers clear, step - by - step instructions.
Understand the Wiring: It usually has two wires for triggering the door release.
3. Installation Precautions
A. Electrical Safety
Turn Off the Power: Before starting the installation, disconnect the power supply to the access control system.
Check the Voltage: Make sure the voltage matches the requirements of the exit button.
B. Proper Wiring
Avoid Short Circuits: Use wire connectors to insulate the exposed parts of the wires.
Label the Wires: Clearly mark the wires according to the system diagram.
C. Physical Installation
Choose the Right Location: Install the button at a height of 1.2 - 1.5 meters for easy access.
Ensure Stability: Secure the button firmly to prevent it from shaking or coming loose.
D. Waterproofing (for Outdoor Use)
Use Sealants: Apply silicone sealant around the edges of the button if it's going to be installed outdoors.
Opt for IP66 Models: Select weatherproof models for outdoor installations.
E. System Compatibility
Verify Compatibility: Confirm that the exit button is compatible with your Tuya access control system.
Update Firmware: Keep the firmware of the access control panel up - to - date.
4. Troubleshooting Tips
Non - Responsive Button: Check the wiring connections and the power supply.
Intermittent Operation: Tighten the screws and clean the contact points.
Unexpected Locking: Review the system settings for any anti - passback configurations.
5. When to Seek Professional Help
Complex Systems: If you're dealing with multi - door systems or advanced access control setups, it's best to consult a professional.
Warranty Concerns: Improper installation may void the warranty, so seek professional help if you're unsure.
User - Friendly Design: The intuitive layout simplifies the installation process.
Versatile Compatibility: It can work with various Tuya access control devices.
Durable Construction: Made from flame - retardant materials, ensuring long - lasting use.
By following these guidelines, you can safely and efficiently install the S4A Tuya Exit Button and enjoy seamless access control. For more detailed information, visit S4A factory's Installation Guide or get in touch with S4A support team.

Author: Written by Ms.Anna Zhang from S4A INDUSTRIAL CO., LIMITED