Is RO4725JXR the Optimal Cost-Effective Solution for Your High-Frequency PCB Design Needs?
Is RO4725JXR the Optimal Cost-Effective Solution for Your High-Frequency PCB Design Needs?
In the rapidly evolving world of wireless communication, the demand for high-performance, reliable, and cost-effective printed circuit boards (PCBs) is greater than ever. For engineers and designers working on cutting-edge RF and antenna systems, the choice of substrate material is critical. RO4725JXR high-frequency PCB emerge as a premier solution, expertly engineered to meet the stringent requirements of modern high-frequency applications while offering exceptional value and manufacturability.
Introduction to RO4725JXR High-Frequency Laminates
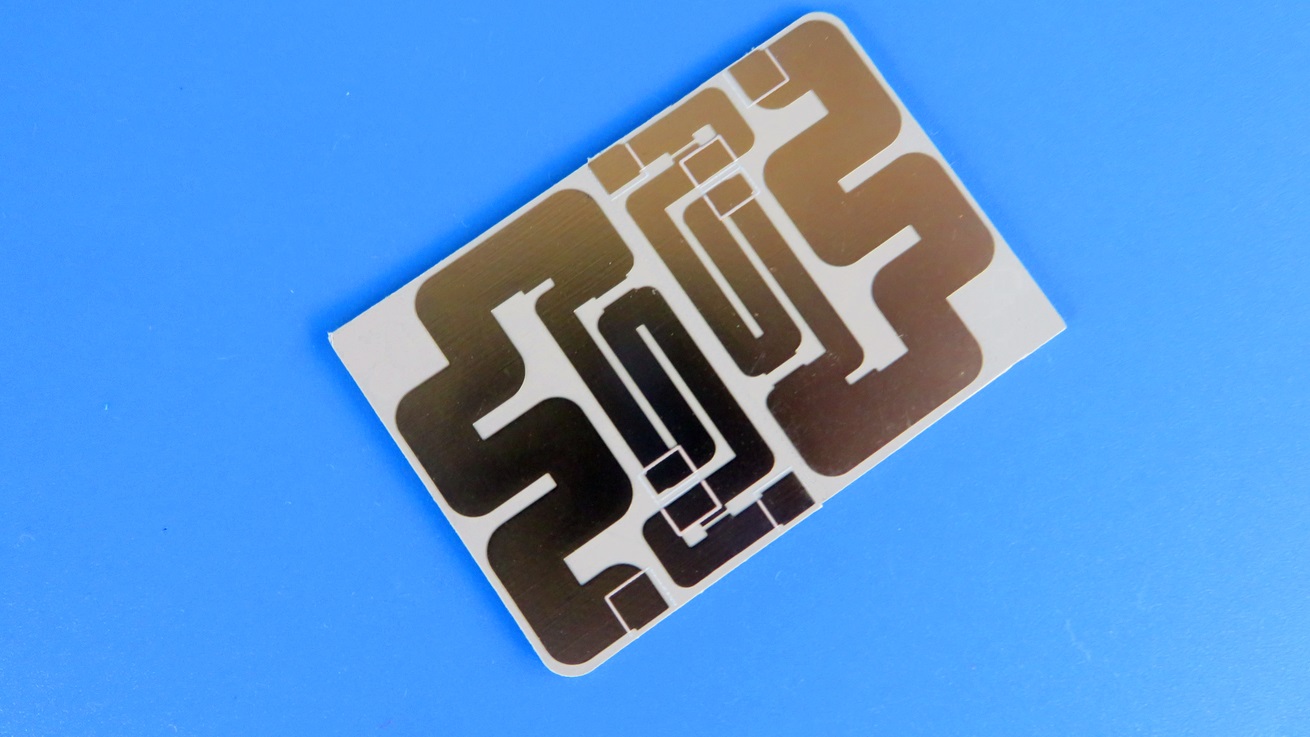
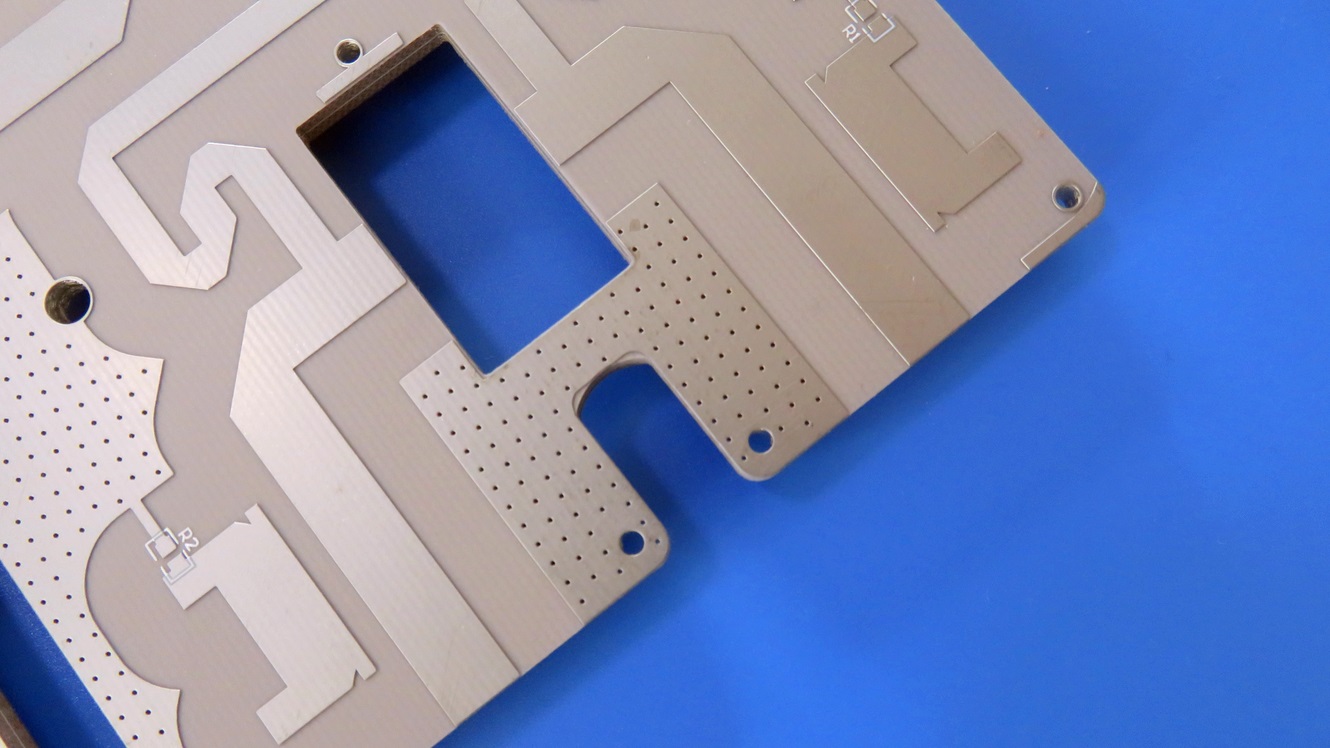
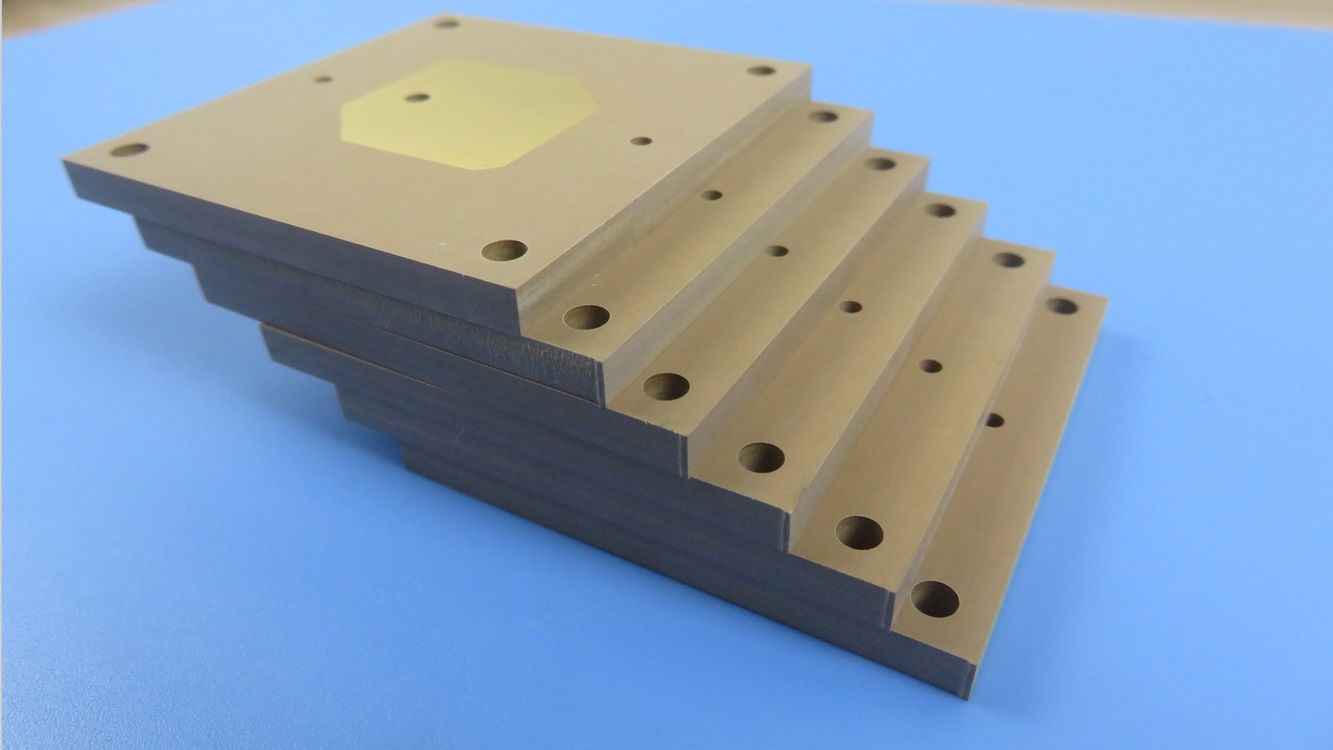
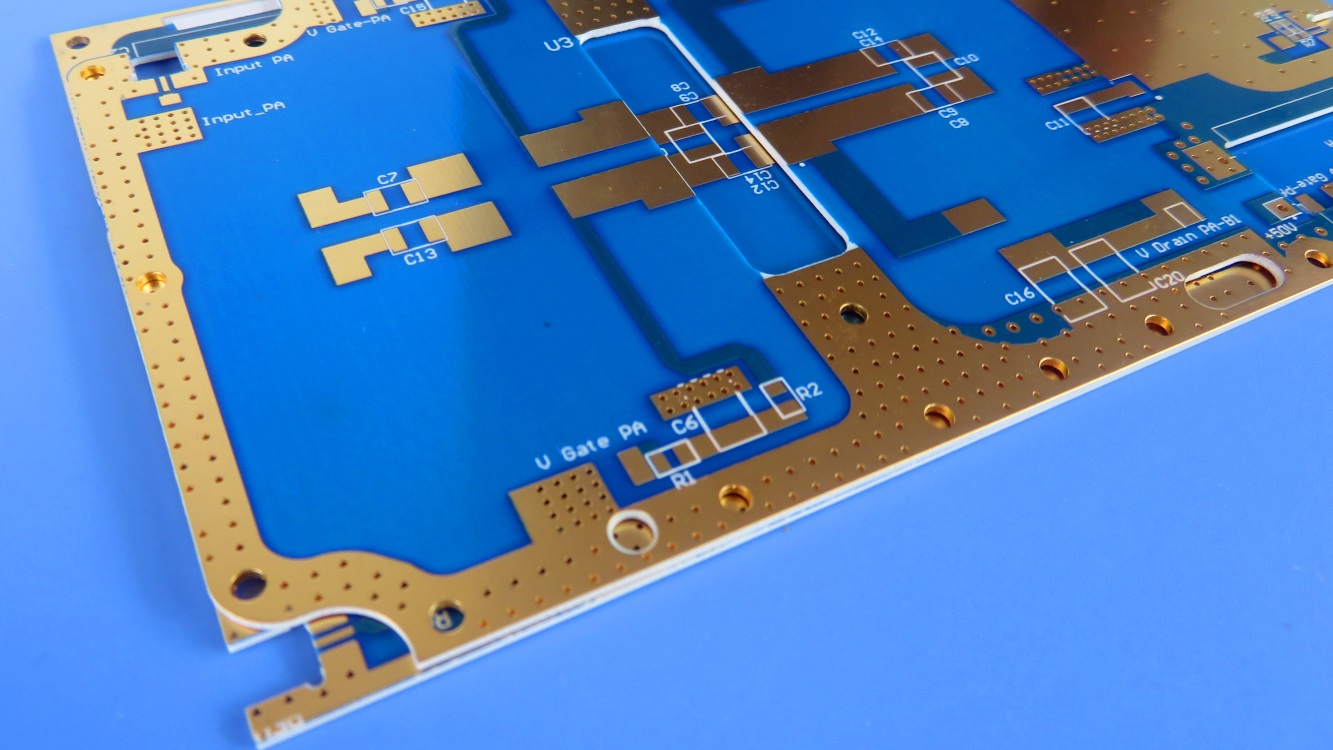
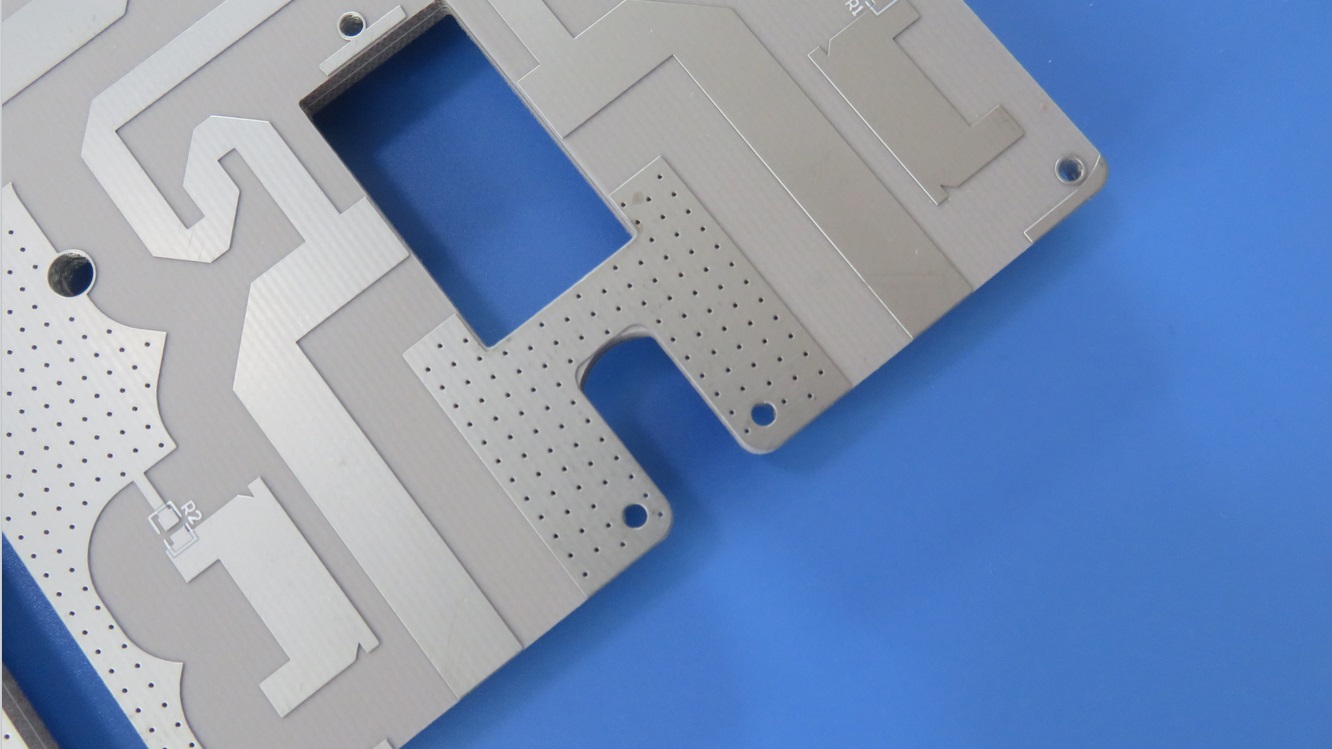
RO4725JXR is an antenna-grade laminate constructed from a sophisticated composite of hydrocarbon, ceramic, and woven glass. This unique formulation endows the dielectric material with a suite of properties that are indispensable for optimal antenna performance. A significant advantage of Rogers RO4725JXR is its full compatibility with standardFR-4 multilayer board processing and high-temperature lead-free assembly workflows. Unlike traditional polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) based materials, which often necessitate specialized and costly through-hole preparation treatments, RO4725JXR PCB simplifies the manufacturing process. This elimination of extra steps positions it as a highly cost-competitive alternative to conventional PTFE antenna materials, allowing design engineers to strike a perfect balance between superior radio frequency performance and overall project budget.
Outstanding Material Properties and Features
The superiority of RO4725JXR is defined by its exceptional electrical and thermal characteristics, each contributing to enhanced signal integrity and reliability in high-frequency environments.

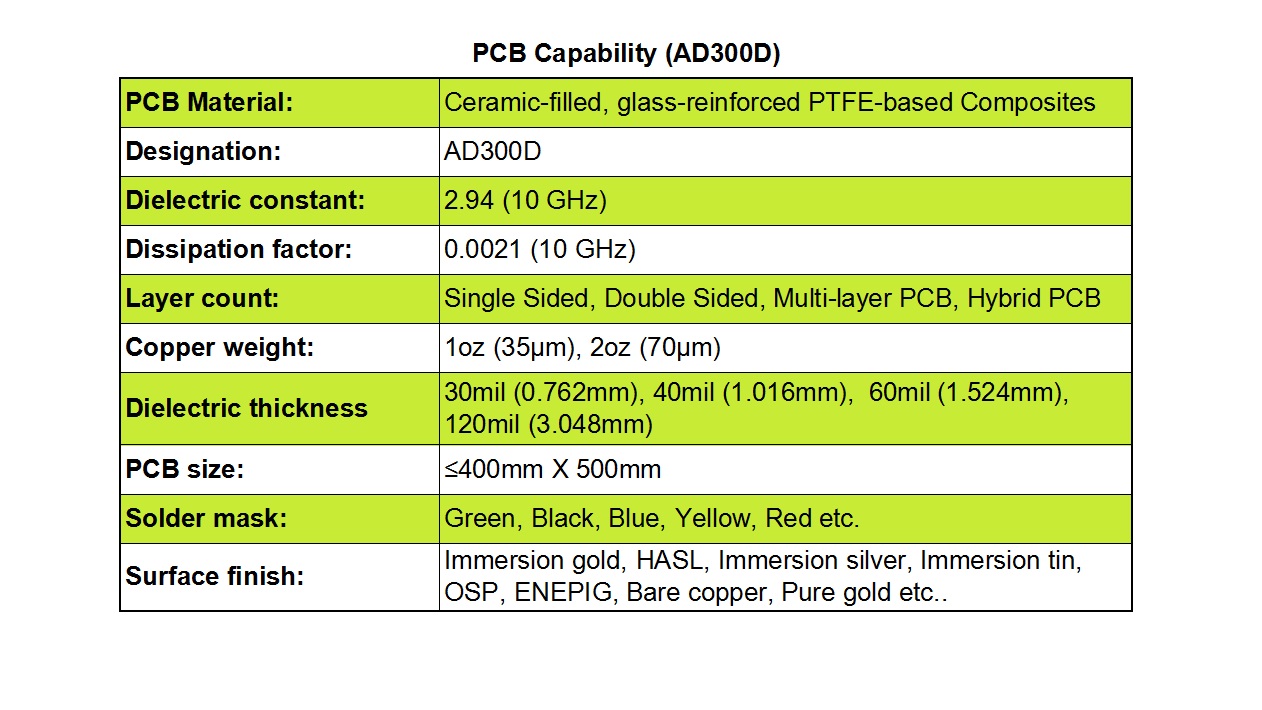
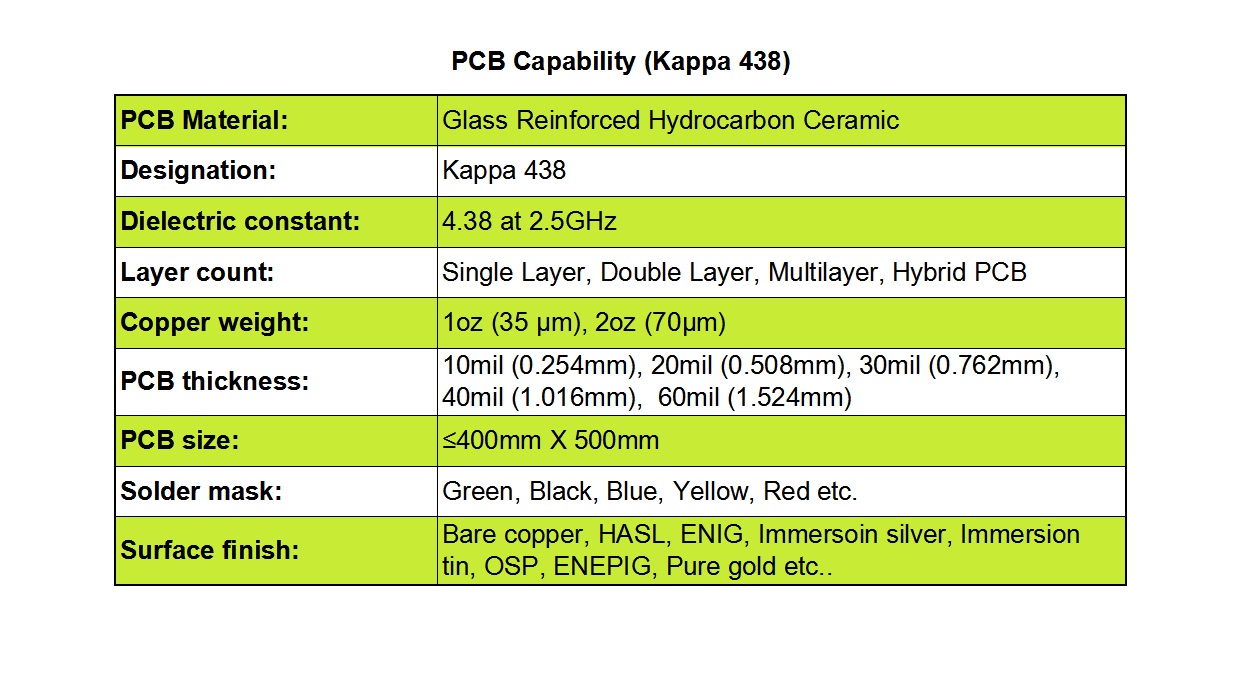
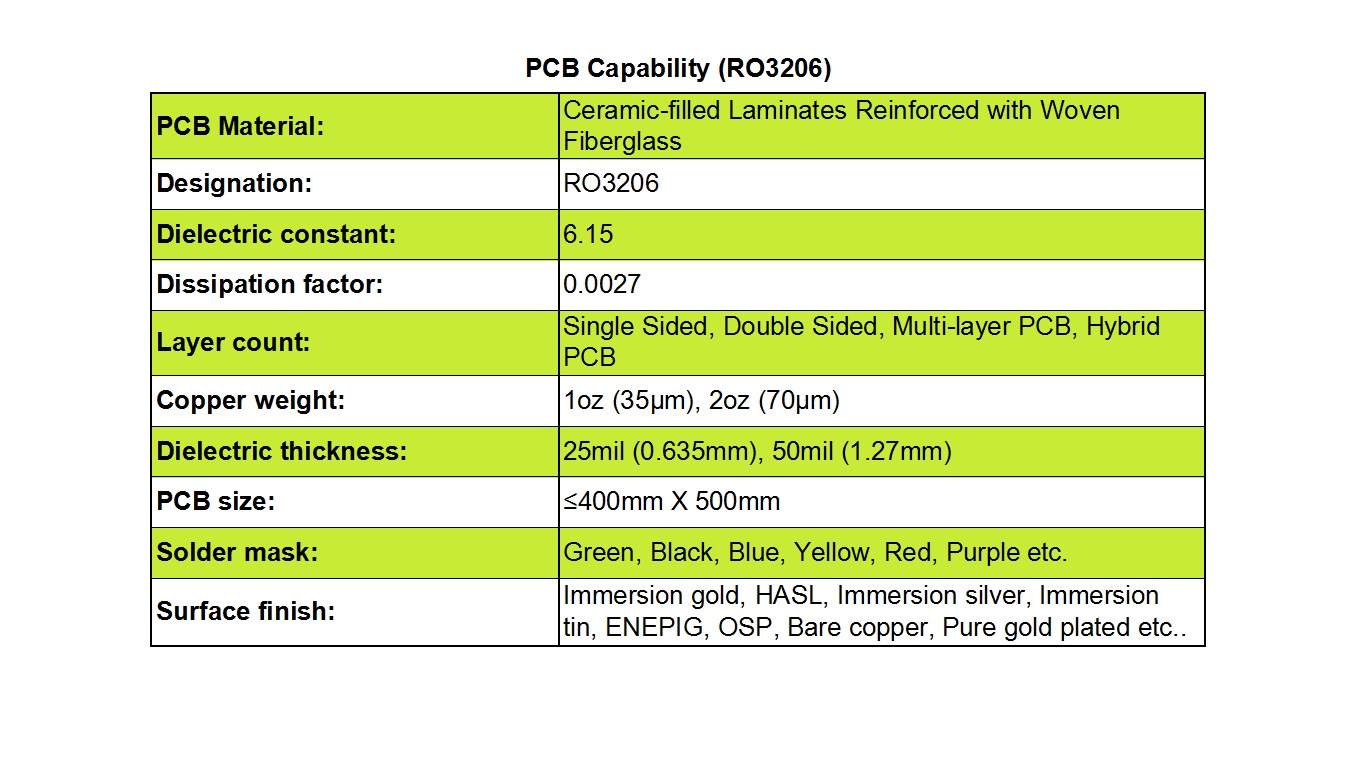
1) Controlled Dielectric Constant (Dk): RO4725JXR boasts a low and exceptionally stable dielectric constant of 2.55±0.05, measured at 10 GHz. This precision ensures consistent impedance control and minimizes signal propagation delays, which is vital for maintaining signal fidelity in high-speed RF circuits.
2) Low Z-Axis Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): With a Z-axis CTE of 25.6 ppm/°C, the material demonstrates remarkable dimensional stability across a wide temperature range. This property is crucial for preventing via failures, as it significantly reduces the risk of plated through-holes cracking during thermal cycling, thereby enhancing the long-term reliability of the PCB assembly.
3) Excellent Thermal Coefficient of Dk (TCDk): The thermal coefficient of the dielectric constant is a remarkably low +34 ppm/°C. This ensures that the electrical properties of the material remain stable and predictable even as operating temperatures fluctuate, preventing performance drift in critical applications.
4) Minimal Dissipation Factor (Df): At 10 GHz, the laminate exhibits an ultra-low dissipation factor of just 0.0026. This low loss tangent translates to minimal signal energy being lost as heat, thereby improving efficiency and enabling clearer signal transmission over longer distances with reduced attenuation.
5) High Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): Featuring a Tg exceeding 280°C, RO4725JXR retains its mechanical rigidity and electrical properties even when subjected to the high temperatures encountered during lead-free soldering and harsh operational conditions.
6) Reduced Passive Intermodulation (PIM): A standout feature for antenna applications is its superior Passive Intermodulation performance, with a typical PIM value of -166 dBC. This low PIM is essential for minimizing interference and maintaining signal clarity in high-power multi-carrier cellular antenna systems, directly boosting overall antenna performance.
Comprehensive PCB Manufacturing Capabilities
To fully leverage the advantages of RO4725JXR material, our manufacturing services offer extensive capabilities tailored to your specific project requirements.
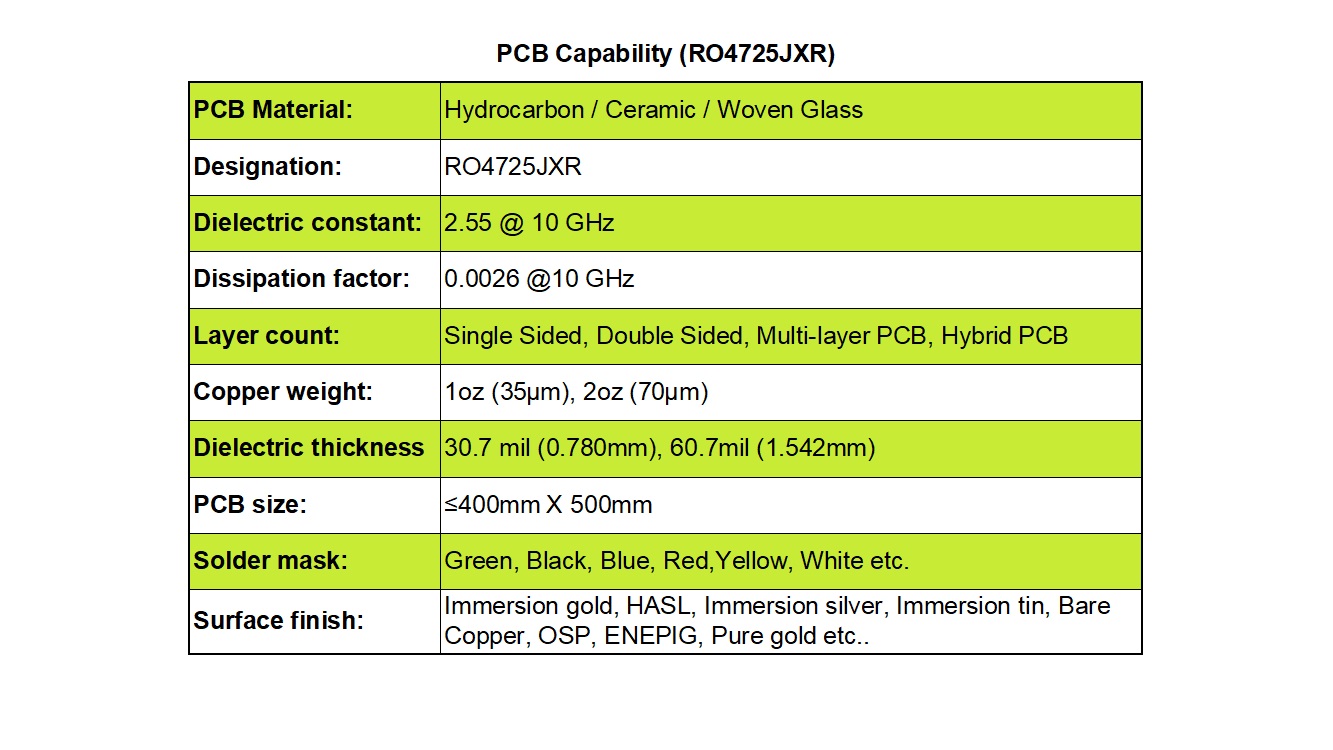
We provide a complete range of PCB constructions, from simple single-sided and double-sided boards to complex multi-layer and hybrid designs. This versatility makes our services ideal for everything from basic electronic devices to sophisticated communication infrastructure.
To achieve precise impedance matching, we offer various dielectric thickness options, including 30.7 mil and 60.7 mil, providing the flexibility needed to meet diverse signal requirements. Furthermore, copper weight is customizable, with standard options like 1oz (35 µm) or 2oz (70 µm), allowing for the optimization of current carrying capacity and electrical performance.
Our production panels can accommodate boards up to 400 mm x 500 mm in size. This generous panel size is perfect for large-format applications and allows for the integration of multiple components and subsystems, offering greater design flexibility and economies of scale.
Aesthetically and functionally, we provide a wide selection of solder mask colors, including green, black, blue, red, yellow, and white. To protect the copper circuitry and ensure superior solderability, we also offer a comprehensive array of surface finishes. These include Immersion Gold (ENIG), Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL), Immersion Silver, Immersion Tin, OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative), ENEPIG, and even Pure Gold plating.
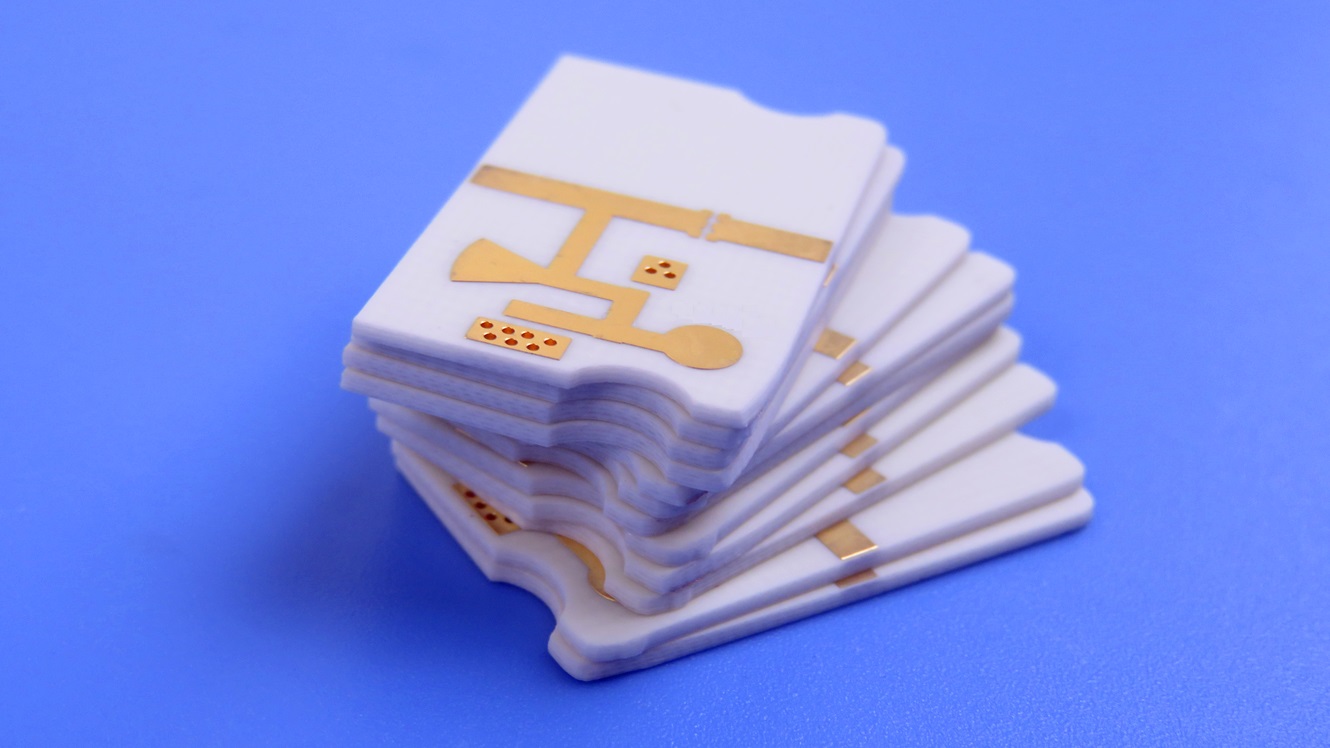

Primary Applications
The combination of its electrical properties and reliability makes the RO4725JXR Rogers PCB the material of choice for a variety of demanding RF applications. It is most commonly deployed in cellular base station antennas, where its low loss and superb PIM performance are critical for supporting 4G LTE and 5NR networks. Beyond this, it is also highly suitable for other wireless infrastructure, satellite communication systems, and a broad spectrum of high-frequency automotive and aerospace radar applications.
By choosing RO4725JXR, you are not just selecting a PCB material; you are investing in a solution that guarantees performance, durability, and cost-efficiency for your most advanced high-frequency designs.