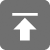
In the intricate world of modern electronics, the stability of an oscillator is paramount, particularly in applications where precise timing and frequency control are critical. While various types of oscillators exist—from LC oscillators and RC oscillators to ceramic resonators—the crystal oscillator stands out as the undisputed champion when it comes to stability. Its superior performance stems from the unique properties of piezoelectric quartz crystals, making it an indispensable component in sophisticated systems like Energy Management Systems (EMS) and Battery Management Systems (BMS).
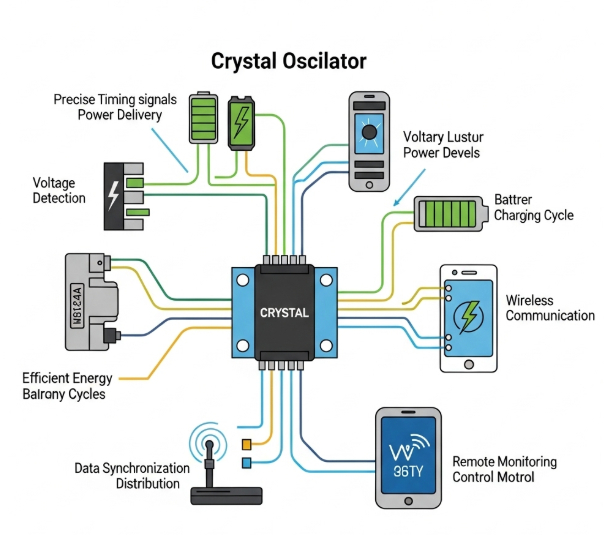
The Heart of Stability: Crystal Oscillator Working Principle
At its core, the exceptional stability of a crystal oscillator lies in the crystal oscillator working principle. These devices utilize the piezoelectric effect, a phenomenon where certain materials generate an electric charge in response to applied mechanical stress, and vice versa. Quartz, being a naturally piezoelectric material, vibrates at a precise resonant frequency when an alternating voltage is applied across it. This mechanical resonance is incredibly stable, much more so than the electrical resonance in LC or RC circuits, which are more susceptible to temperature fluctuations, voltage changes, and component aging.
The quartz crystal acts as a highly selective filter, allowing only a very narrow range of frequencies to pass through. When integrated into an oscillating circuit, the crystal's natural resonance dictates the oscillation frequency. Any deviation from this frequency is strongly suppressed by the crystal's high Q-factor (quality factor), leading to extremely stable and accurate output. This inherent stability makes the crystal oscillator the preferred choice for applications demanding unwavering precision.
Essential Roles in Energy and Battery Management Systems
The precise timing offered by crystal oscillators is not merely a technical advantage; it's a fundamental requirement for the reliable operation of critical systems like EMS and BMS.
In Energy Management Systems (EMS):
EMS are designed to optimize energy usage, monitor power flow, and ensure the efficient distribution of electricity. Within an EMS, crystal oscillators play a crucial role in several areas:
Accurate Voltage and Current Sensing: Precise timing from crystal oscillators is vital for the accurate sampling and digitization of voltage and current signals. This allows the EMS to obtain real-time, high-fidelity data on power consumption and generation, enabling efficient load balancing and fault detection. Without stable timing, these measurements would drift, leading to inaccurate energy assessments and potentially costly operational inefficiencies.
Data Synchronization: Modern EMS often rely on distributed sensors and control units that need to communicate and synchronize data across a network. High frequency crystal oscillator units provide the stable clock signals necessary for robust data communication protocols, ensuring that all components within the system operate in perfect unison. This synchronization is critical for tasks like demand-side management, where timely responses to grid conditions are essential.
Time-Sensitive Control Algorithms: Many energy management algorithms, such as those for smart grids and renewable energy integration, are highly time-sensitive. The consistent clock provided by a crystal oscillator ensures that these algorithms execute precisely when needed, leading to optimal energy dispatch and minimal waste.
In Battery Management Systems (BMS):
BMS are responsible for overseeing the performance and safety of battery packs, particularly in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and grid-scale energy storage. The reliability of a BMS is directly tied to the stability of its timing components.
Precise Cell Voltage Detection: Accurate measurement of individual cell voltages is paramount in a BMS to prevent overcharging or deep discharging, which can severely degrade battery life or even lead to hazardous conditions. Crystal oscillators provide the stable time base required for Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) to sample these voltages with high precision, ensuring optimal battery health and longevity.
Current Monitoring and State-of-Charge (SoC) Calculation: Just like voltage, accurate current measurement is crucial for calculating the battery's State-of-Charge (SoC) and State-of-Health (SoH). The stable clock from an oscillator crystal ensures reliable current sensing, which in turn leads to more accurate SoC estimations and a better understanding of the battery's remaining capacity.
Thermal Management Synchronization: Many BMS employ active thermal management strategies, involving sensors and cooling/heating elements. The synchronized operation of these components, facilitated by crystal oscillators, ensures that the battery pack maintains an optimal operating temperature, preventing thermal runaway and maximizing performance.
Wireless Communication: For wireless BMS or those communicating with external systems, stable frequency generation is essential for reliable radio frequency (RF) communication. Whether it's Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or proprietary wireless protocols, the underlying clock for these transceivers often relies on a crystal oscillator to maintain signal integrity and prevent data loss.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer and Type
When it comes to selecting a crystal oscillator, partnering with a reputable crystal oscillator manufacturer is crucial. Companies with extensive experience and stringent quality control processes can ensure the reliability and long-term stability of their products. For instance, manufacturers like JGHC are recognized for their expertise in producing high-quality crystal components that meet the demanding requirements of industrial and automotive applications.
The specific type of crystal oscillator chosen will depend on the application's needs. While standard crystal oscillators offer excellent stability for many applications, more demanding environments might require temperature-compensated crystal oscillators (TCXOs) or oven-controlled crystal oscillators (OCXOs). TCXOs minimize frequency drift over a wide temperature range, while OCXOs provide even higher stability by maintaining the crystal at a constant temperature within a miniature oven. For very high-frequency applications, surface acoustic wave (SAW) oscillators might be considered, though their stability typically doesn't match that of traditional quartz crystal oscillators.
Beyond Stability: Other Considerations
While stability is the primary advantage of crystal oscillators, other factors also contribute to their widespread adoption:
Low Phase Noise: Crystal oscillators exhibit low phase noise, which refers to random fluctuations in the phase of the output signal. Low phase noise is critical in communication systems where it can otherwise degrade signal quality and increase error rates.
High Q-Factor: As mentioned earlier, the high Q-factor of quartz crystals contributes directly to their sharp resonance and excellent frequency selectivity. This inherent property makes them less susceptible to external interference and noise.
Long-Term Reliability: When properly manufactured and integrated, crystal oscillators are known for their exceptional long-term reliability and minimal frequency drift over their operational lifespan. This makes them ideal for mission-critical applications where maintenance or replacement is difficult or costly.
In conclusion, the crystal oscillator emerges as the most stable oscillator due to the inherent properties of quartz crystals and their superior piezoelectric effect. This stability is not merely an academic concept but a practical necessity, especially for the accurate voltage detection, data synchronization, and reliable wireless communication crucial for the effective operation of Energy Management Systems and Battery Management Systems. As electronics continue to evolve, the demand for ever more precise and stable timing components will only grow, solidifying the crystal oscillator's position as a cornerstone of modern technological advancement.